Python Interpreter

To run your Python programs, you need a Python interpreter. There are different versions of the Python interpreter; any recent enough version will be sufficient for the purposes of this course. Just make sure to install one that is version 3.11 or higher and add some packages used during the course.
Installing Python
The installation of Python depends slightly on your operating system:
You will most likely already have it installed
For this course, you do not need to install Python with other distributions like Anaconda or Spyder. In fact, I recommend that you do not.
Once you have Python installed, verify that it works well from your terminal application:
TODO: add link to terminal course
- Open a terminal (see the course The Terminal (/terminal/index.html) for more information).
- Run the command
pythonorpython3or something likepython3.11. - Verify that the command loads the version of Python you installed.
- Exit the interpreter with the command
exit().
Installing additional packages
Now it is advisable to add some additional packages that we will use during the course: These are yogi (a package to simplify data reading), numpy (a package for working with vectors), and mypy (a tool to find errors in programs). To do this, run
pip install yogi numpy mypyInstead of pip, you might need to use pip3 or pip3.11 (usually the pattern matches the python command).
Verify that they have been installed correctly:
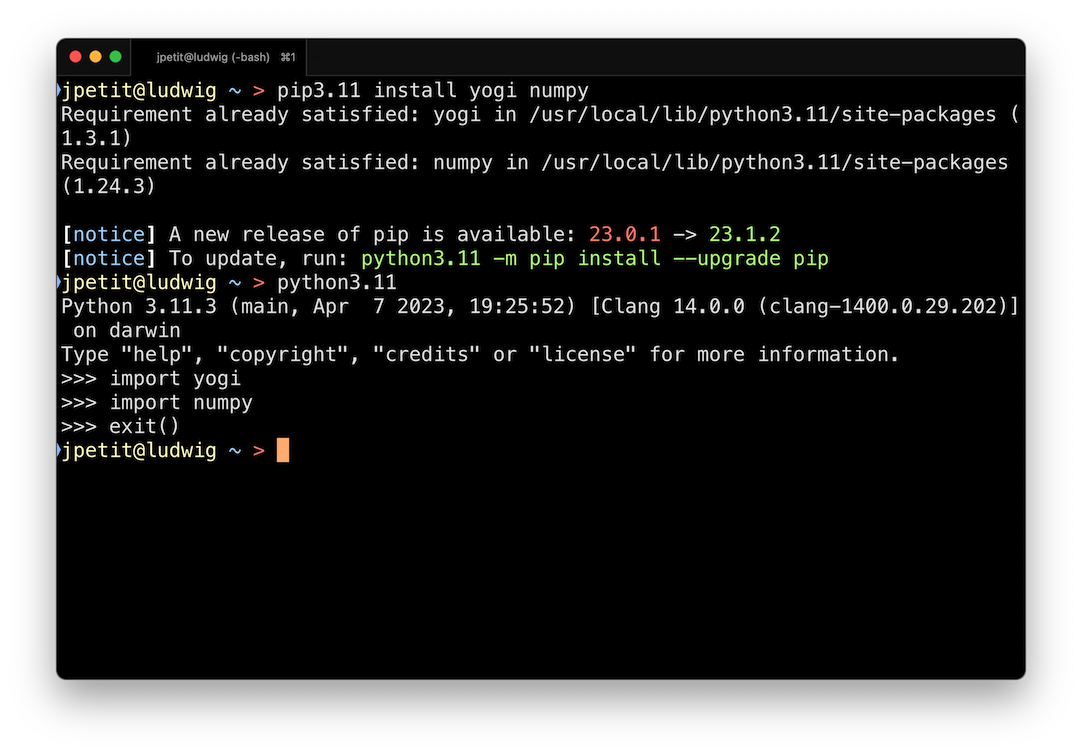
If the imports do not complain, everything has gone well.

Jordi Petit
Lliçons.jutge.org
© Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2026
